What Is a Resistive Touch Screen?
A resistive touch screen is a touch-sensitive computer display that responds to applied pressure. It’s made from two resistive-coated transparent sheets separated by a small air gap.
How Do Resistive Touch Screens Work?
When contact is made with the surface of the touch screen, the two sheets are pressed together. Each sheet has horizontal and vertical conductive traces (also known as bus bars) that register the precise location of the touch, recognizing input from various objects such as fingers, stylus or palms. Resistive touch screens are considered a passive technology. This means they must have an internal power source and rely on electromagnetic energy transmitted from an RFID (radio-frequency identification) reader.
Components of a Resistive Touch Screen
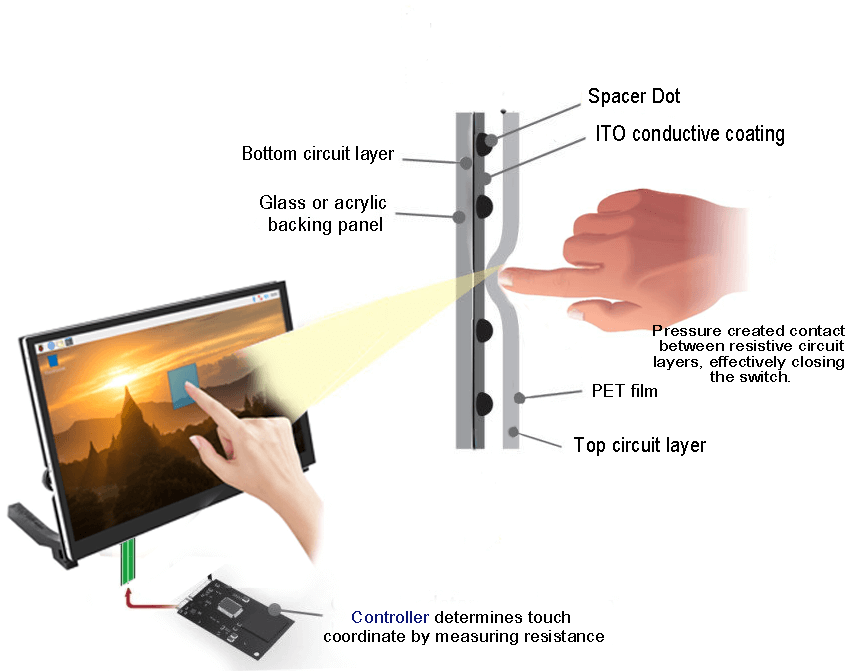
Top Layer (Flexible Clear Film)
Function: The top layer is a clear, flexible film made of polyester or a similar material. It is the outermost layer, which users physically interact with.
Control: The top layer is responsible for detecting touch inputs. When pressure is applied, this layer deforms, causing it to make contact with the layer beneath.
Spacer Dots or Adhesive Spacer
Function: Spacer dots, or an adhesive spacer, separate the top and bottom layers, maintaining a small air gap between them when there is no pressure applied.
Control: The spacer ensures that the layers do not make contact when not pressed, preventing false touch signals.
Bottom Layer (Glass or Hard Plastic)
Function: The bottom layer is typically a rigid material such as glass or hard plastic.
Control: The bottom layer carries a resistive coating that registers touch points when the top layer is pressed against it. The resistive coating divides the layer into rows and columns, forming a grid for precise location detection.
Resistive Coating
Function: Both the top and bottom layers have a resistive coating, usually made of indium tin oxide (ITO).
Control: The resistive coating is conductive and facilitates the measurement of changes in electrical current when the top layer makes contact with the bottom layer. This change in resistance helps determine the touch location.
Bus Bars (Conductive Strips)
Function: Bus bars are conductive strips made of a transparent material, often positioned on the edges of the layers.
Control: The bus bars help transmit electrical signals from the resistive coating to the touch controller, facilitating communication between the touch screen and the device’s controller.
Touch Controller
Function: The touch controller is an electronic component that processes the touch input signals and translates them into digital data.
Control: The touch controller interprets the changes in resistance and converts them into X and Y coordinates, determining the precise location of the touch on the screen. It then sends this data to the device’s processor.
What Are the Different Types of Resistive Touch Screens?
There are two types of resistive touch screens:
-
Digital
-
A digital resistive touch screen operates through the application of pressure to the screen, and can be operated by the touch of a finger, stylus or even a fingernail onto the surface. This type of touch screen works on an X-Y matrix.
-
-
Analog
-
Analog touch screens respond to continuous and variable pressure. They are designed for pen recognition applications and can offer higher resolutions.
-
What Are the Advantages of Resistive Touch Screens?
Very Cost-Effective
Resistive touch screen technology tends to be more cost-effective compared with some other touch screen technologies, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious applications. Some applications where resistive touch screens are used are ATM machines, vending machines and home appliances.
Easy to Integrate
The design simplicity and versatility of resistive touch screens make them easy to integrate into a design. Resistive touch screens are compatible with a variety of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, Android and others. They typically use standard interfaces, such as USB or serial connections. Most resistive touch screens come with drivers that are readily available and supported by major operating systems. These factors make integration easy, fast and efficient.
Can Be Operated with Numerous Touch Signals
Resistive touch screens are pressure-sensitive, allowing them to register varying levels of pressure applied to the screen by virtually any point of contact. This feature is especially useful in applications where the user might be wearing gloves that would hinder pushing a mechanical button.
Resistant to Dust, Moisture and Humidity
Resistive touch screens offer a degree of resistance to dust, moisture and humidity, but their level of protection can vary based on the specific design and construction of the touch screen. Since resistive touch screens have a continuous top layer, any moisture or contaminants need to enter on the edge or around the screen. A bezel that overlaps the edge of the screen with a gasket using quality adhesives or sealant will ensure a good seal. This is especially important in dusty, wet or dirty environments.
What Are the Drawbacks of Resistive Touch Screens?
Can Be Prone to Damage
The flexible layers of resistive touch screens are subject to wear and tear over time, especially in high-use environments or when rough or sharp objects are used to actuate the screen. Continuous pressure on the screen can lead to degradation and reduced sensitivity over-time. The top layer of a resistive touch screen is typically made of a flexible clear film, which can be susceptible to scratches. This vulnerability can affect the clarity of the display and compromise the touch screen’s functionality. Once the screen is damaged, there are no good ways to repair it to full functionality without replacing the entire screen.
Limited Contrast
The resistive touch screen is typically installed over a digital display panel. The presence of additional layers over the display may cause a reduction in contrast and brightness, affecting the overall visual experience. This limitation is more noticeable in outdoor settings where high visibility is crucial.
Does Not Support Multi-Touch
Traditional resistive touch screens typically support only single-touch input. They do not have the capability to recognize multiple touch points simultaneously, limiting their functionality in applications that benefit from multi-touch gestures. Multi-touch is important for interactive whiteboards, gaming consoles, smartphones and laptops.
Now that we know all about the resistive touch screen technology, let’s take a look at a popular alternative: Capacitive Touch Screens
What Is a Capacitive Touch Screen?
Capacitive touch screen panels share a visual resemblance with resistive touch screens. What sets them apart is their distinctive operation – they respond effortlessly to a gentle touch without requiring applied pressure. The mere touch of a finger induces a small current, creating a voltage drop that activates the screen. This unique mechanism not only ensures user comfort but also contributes to the screen’s longevity by minimizing physical stress.
The structure of capacitive touch screens involves two layers of glass, allowing for superior resolution and the ability to detect multiple touches simultaneously. This multi-touch capability enhances the user experience, providing advanced functionalities for various applications.
While the benefits of capacitive touch screens are evident, it’s worth noting that they typically come at a higher cost due to their intricate structure. However, the investment is often justified by the enhanced performance and durability they offer.
Multitouch capacitive screens, like those found on smartphones, have the capability to detect multiple points of contact simultaneously. This ability is enabled by the design which includes an invisible grid system. Each intersection on the grid is able to individually detect a conductive material, such as a fingertip, allowing for a precise multitouch interaction. .
The Bottom Line:
Understanding the subtle differences among touch screen technologies is crucial in determining the most suitable option for your needs.
Whether you require a digital resistive, analog resistive or capacitive touch screen, RSP stands ready to provide optimal solutions. Our commitment extends to designing and producing each touch screen panel to meet our customers’ specific requirements. Additionally, we offer customized integration solutions for membrane switches, silicone rubber keypads and displays, as well as plastic and metal enclosures, ensuring a seamless and tailored experience for your company.
To find out more about RSP’s high-quality custom touch screens and how they can help your business, contact us at 1-866-329-1804 or send us a message.

